| App Name | Daman Game App |
| Invite Code To Register | 222479906566 |
| Gaming Categories | 10 |
| Daman Game APK Size | 18.8 MB |
Official Daman Game Teacher – https://t.me/CandorJenniferDaman
color prediction games have become a way to earn money. One such game is the Daman game, where you can enjoy a wide range of games including Slot games, WinGo, Mini games and Aviator. Designed for enthusiasts who enjoy testing their analytical skills and luck, Daman Games offers a variety of games such as colour prediction, number guessing, and more. Get the latest version of the Daman game app today by clicking on the link provided.
Why is the Daman Game Loved By Users?
Daman game is played by millions of users daily and is loved by them because of its transparency, wide range of games and security. Some interesting features of the Daman platform include:
-
Variety of Games
Daman Games offers various prediction-based games, including colour prediction, number guessing, and other fun challenges. Players can enjoy diverse options to keep the excitement alive.
-
User-Friendly Interface
Daman game offers you a simple and clean interface, making it easy for players of all skill levels to access and enjoy their favourite games without any difficulty.
-
Secure Transactions
With advanced encryption technology, Daman Games ensures that all deposits and withdrawals are safe and secure, allowing you to make transactions without any worries.
-
Fast Registration Process
Getting started on Daman Games is quick and effortless. By adding some basic information, including your phone number and password, you can get started on the app easily.
-
Mobile-Friendly Platform
Daman Games is optimized for mobile devices, allowing players to enjoy their favourite games anywhere and anytime.
-
Exciting Bonuses and Promotions
The platform offers attractive bonuses, rewards, and promotions to enhance the gaming experience for both new and existing users.
-
Real-Time Results
Daman Games provides instant game results, ensuring transparency and keeping the excitement alive with every prediction.
-
24/7 Customer Support
Players can rely on 24×7 customer support available via live chat or email for assistance with any queries or technical issues.
Types Of Games On The Daman Game Online
One thing that everyone loves about Daman games is the wide range of games it offers. From a beginner-friendly game to an advanced-level game, Daman Games has something for everyone.
-
Slots
Spin the reels and try your luck in the vibrant world of slot games.
-
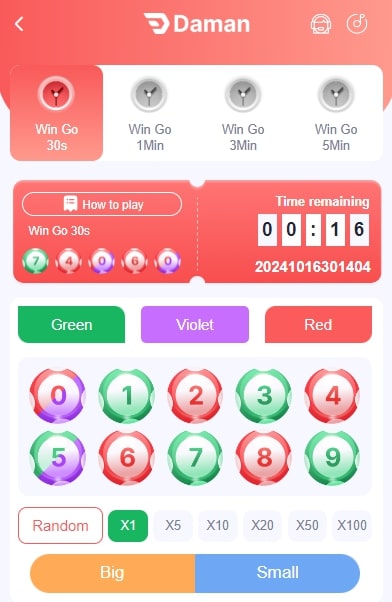
WinGo
WinGo combines luck and strategy in an engaging game that keeps players coming back for more. Predict outcomes, place your bets, and experience the thrill of winning in real time.
-
5D Lotre
Players can select their lucky numbers and test their fortune with thrilling results every round.
-
Aviator
Cash-out before the plane flies away to secure your winnings. This is a game of nerves, strategy, and anticipation!

-
Fishing Games
Catch exotic fish, earn rewards, and enjoy immersive gameplay that brings the ocean to your screen.
-
Mini Games
These games are ideal for players looking to try their luck in fast and short games.
How To Download The Daman Game App?
The Daman game app makes the game easily accessible to users. Once you have an account on the Daman game online platform, you can directly download the app from there.
There are two ways to download the Daman app, including:
Method 1: From The “Add To Desktop” Option
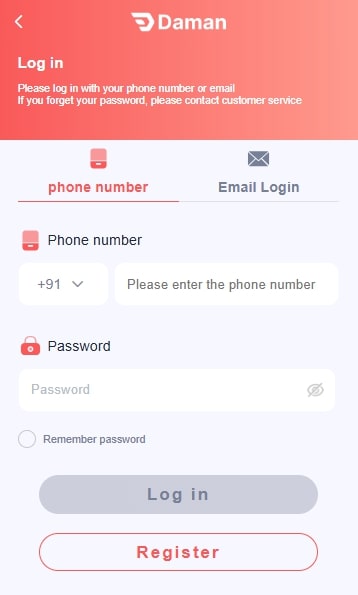
- Login to your Daman game account.
- Click on the “Add to Desktop” option appearing just above the “Promotions” tab.
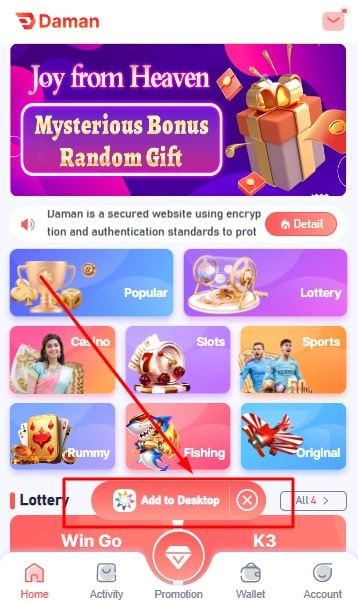
- The file will now start downloading on your device.
- Go to the settings app of your mobile and click on the “Privacy” section.
- Click on the “Unknown sources” option and enable it.
- Look for the downloaded file and click on it to begin installation.
- Once installed, you can start playing.
Method 2: From The Home Screen
- Login to your Daman game account.
- Scroll down on the home page and click on the download app option.
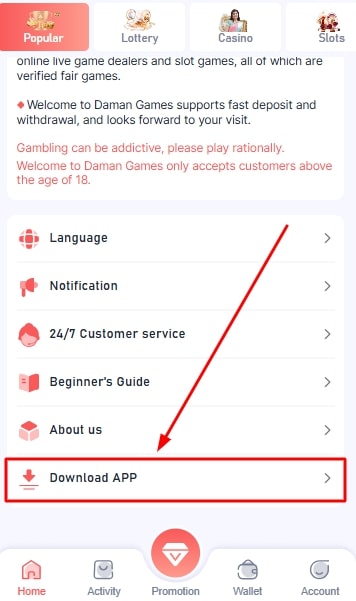
- Open the settings app on your phone and go to the “Privacy” option.
- Click on the “Unknown sources” option and allow it.
- Now, tap on the file that you have downloaded and begin installation.
How To Create An Account On The Daman Game Online?
It is very easy and will take a few seconds to create an account on the Daman online game. Here’s how you can get started on the platform:
- Go to the official Daman game website.
- Click on the register button.
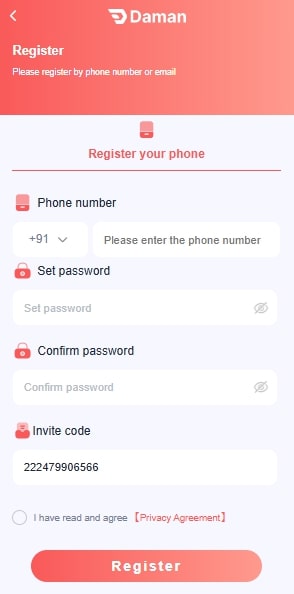
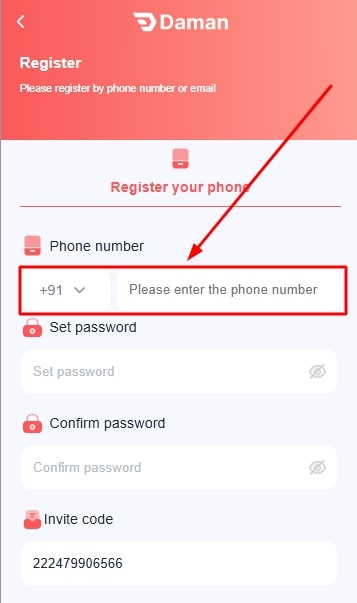
- Type your mobile number. Make sure this number isn’t already registered on the platform.
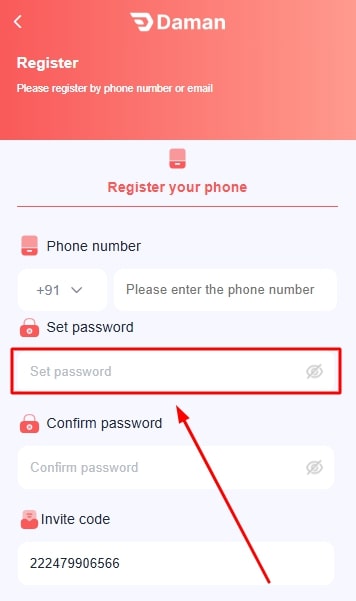
- Type your password and confirm the same in the next field.
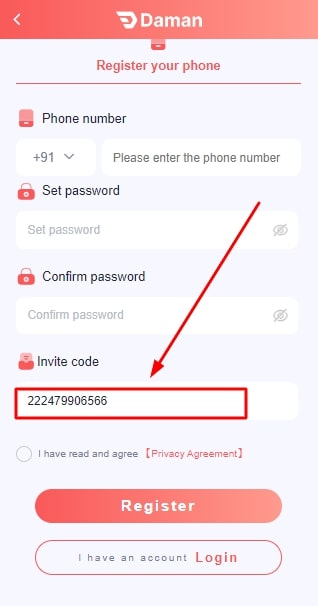
- If you have any invitation code, enter the same.
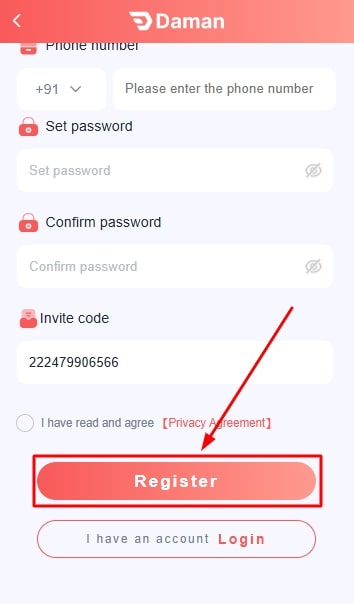
- Agree to terms and conditions.
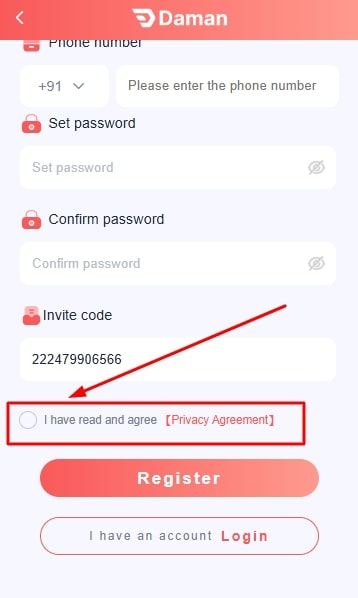
- Click on register to create the account.
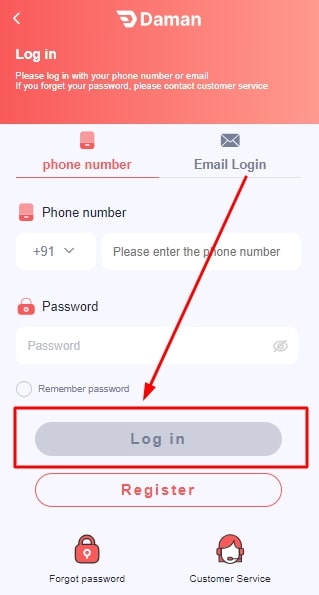
How To Login To Your Daman Game Account?
To log in to the Daman account, follow the steps listed below:
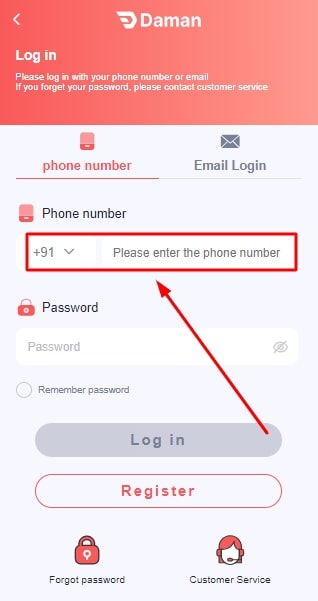
- Open the Daman game app or the website.

- Enter your registered mobile number.
- Type your password.
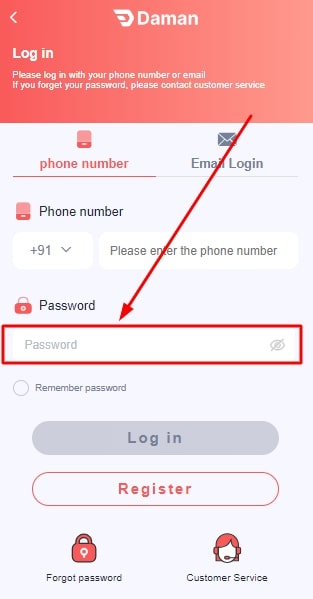
- Click on Login.
How To Add Funds To The Daman Game Account?
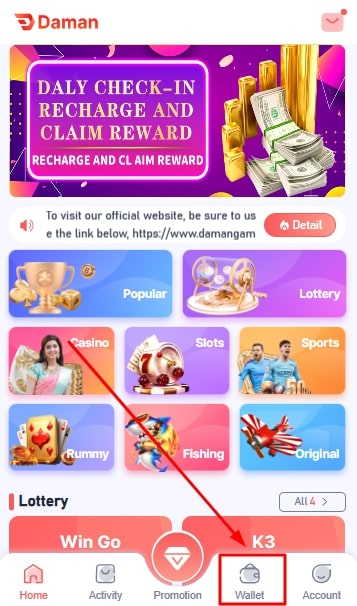
Before you start playing and betting on the Daman app, you need to add funds to your account. Here is how you can do it:
- Sign in to your Daman account.
- Go to the wallet section.
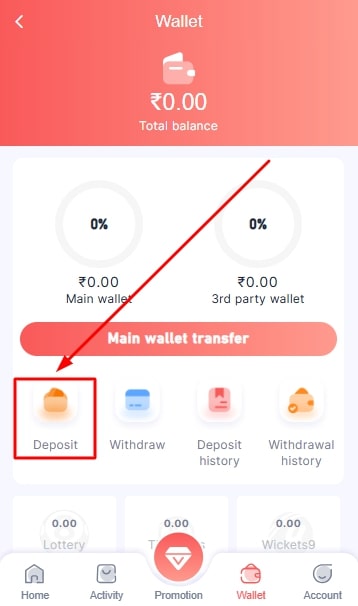
- Click on the “Deposit” option.
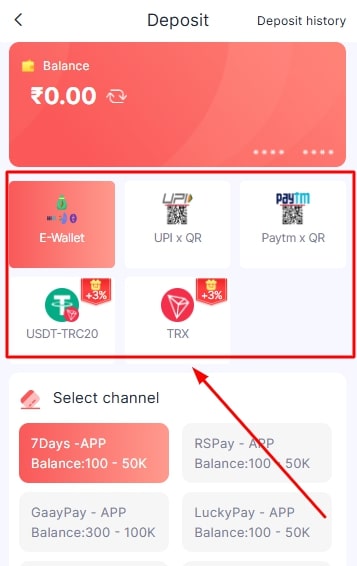
- Select the payment method.
- Enter the amount you wish to add to your Daman game account.
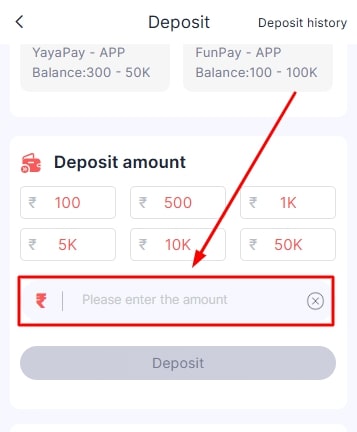
- Click on the deposit button after confirming all the details.
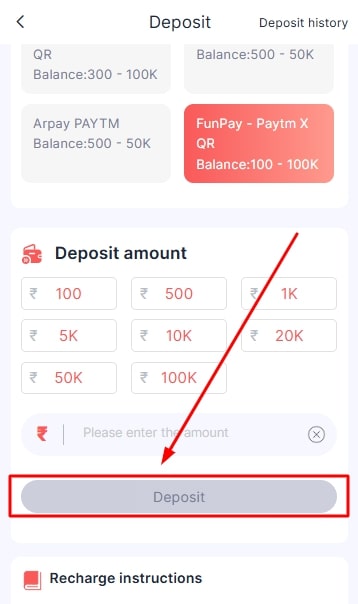
- Once done, the amount will start reflecting in your Daman game online account.
How To Withdraw Money From The Daman Account?
You can withdraw a minimum of INR 100 and a maximum of INR 10000 from the Daman game account. Here are the steps to withdraw money from the Daman game account:
- Login to your Daman online game account.
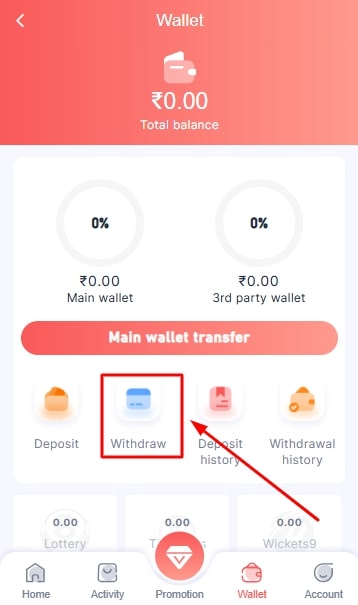
- Click on the Wallet option.

- Choose the “Withdrawal” option.
- Add your bank account if you haven’t. If you already have it, select your bank account.
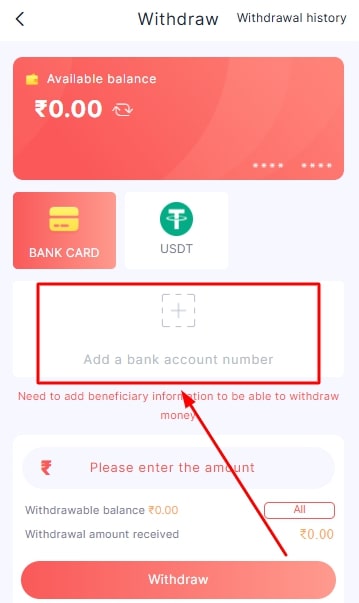
- Type the amount you wish to withdraw.
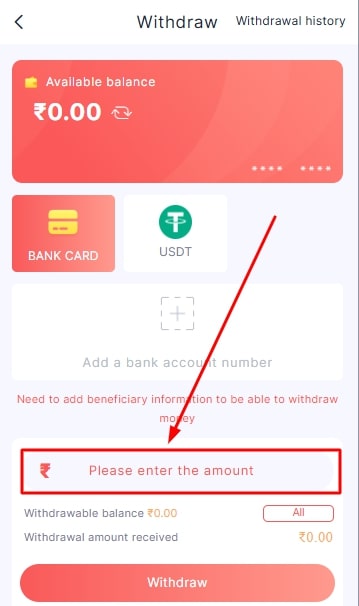
- Once done, click on the withdraw option.
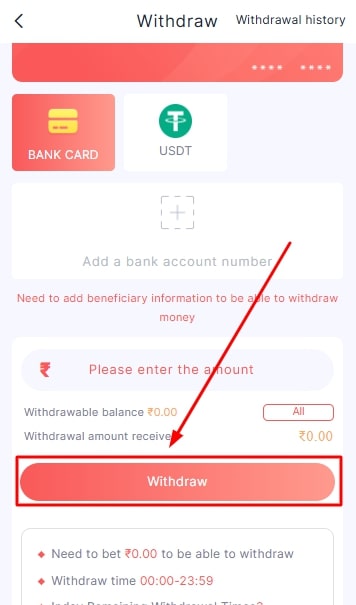
- Enter your account password.
- The amount will take up to 24 hours to reflect in your account.
Daman Game Promote Mission (Refer and Earn Program)
The Daman game promote mission is Same As 91 Club, launched for existing players on the Daman app and it gives them a way to earn some additional money. In this mission, you have to promote the Daman app and once someone joins the platform using your referral code, you can earn money for it.
New to the Daman game promote mission? Check out the steps listed below:
- Login to the Daman game account.
- Go to the Promotion account.
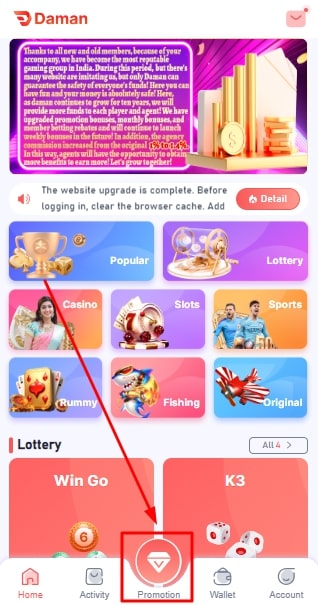
- Tap on the “invitation link” option and click on it to copy the same.
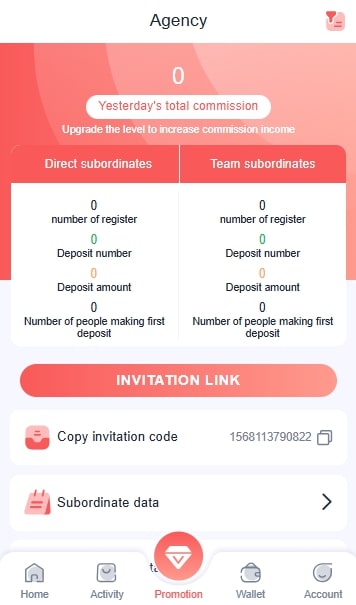
- Share the link among your friends and network.
Conclusion
Daman Games is the perfect blend of entertainment, strategy, and opportunity. With its diverse range of prediction-based games, user-friendly platform, secure transactions, and exciting rewards, it provides a fun and interactive gaming experience. Download the Daman game today and enjoy playing your favourite games anywhere anytime.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
How can I register at Daman Games?
To register, visit the official Daman Games website or app, click on the “Sign Up” button, and fill out the required details like your mobile number and password. Once registered, you can start exploring the games.
-
Is Daman Games safe and secure?
Yes, Daman Games uses advanced encryption and security protocols to ensure all your transactions and personal data are safe.
-
How can I withdraw my winnings?
To withdraw your winnings, go to the “Wallet” section, enter the amount you wish to withdraw, and select your preferred payment method. The withdrawal process is quick and hassle-free.
-
Are there any bonuses or promotions on Daman Games?
Yes, Daman Games offers exciting bonuses and promotions for new and existing users. Check the “Promotions” tab for the latest offers.
-
Can I play Daman Games on my mobile device?
Yes, you can play this game on mobile devices and web browsers.

