Agile Project Management: Principles, Tools, and Benefits
Dive into the dynamic world of Agile project management. It’s not just a methodology but a mindset that revolutionizes the way you manage projects. From its history to its core values and principles, Agile is a game-changer. Discover how Agile works, its key components, and the six essential steps involved in Agile project management. You’ll learn about its pros and cons and who’s using Agile in their business strategy. Get ready to transition into a more flexible, responsive, and efficient way of managing projects. Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just getting started, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of Agile project management. Let’s explore!
What is Agile project management?
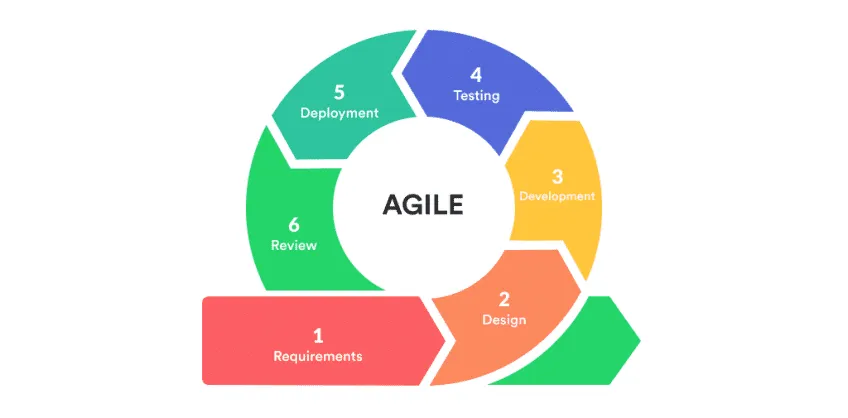
Agile project management refers to the transformative mindset or methodology that’s fostered on the principles of flexibility, efficiency, and, most importantly, responsiveness to changes. A significant aspect attributed to agile project management is the use of agile project management tools and agile project management software. These facilitate the application of agile principles by planning, executing project tasks, tracking progress, and fostering team collaboration.
Agile’s inherent adaptability allows it to easily fit into various business strategies and be customized to meet an organization’s unique needs. Agile rosters have an array of different methodologies under their umbrella, so it’s really about finding the one best suited to your team and project. Some of these include Scrum, Kanban, Lean, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with its distinct features but all maintaining the core concept of iterative development. Agile’s focus on frequent and incremental delivery means you’re consistently offering something of value to the customers, which naturally leads to higher satisfaction.
The 4 Core Values of Agile
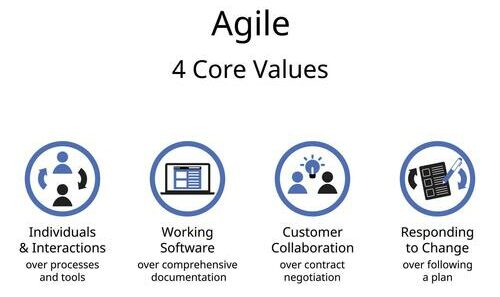
Diving into the heart of Agile project management, let’s unravel its 4 core values. These values, born from the original Agile Manifesto, are not just abstract ideals. They are the gears that drive the agile machine, shaping the way teams work, communicate, and create value.
1. Individuals and Interactions Over Processes and Tools
Agile doesn’t just slap a “one-size-fits-all” set of processes and tools on a team. Instead, it places a higher value on the individuals that make up the team and the interactions between them. As you use agile project management software, you’ll find it’s designed to facilitate these interactions, not replace them.
2. Working Software Over Comprehensive Documentation
Doesn’t it feel more satisfying to deliver a working piece of software than to write a detailed report about how it’ll work? That’s Agile project management in a nutshell, where the goal is functional software that serves the end user’s needs.
3. Customer Collaboration Over Contract Negotiation
This emphasizes the necessity of dialogue with the client. Traditional project management may stress detailed contracts and specifications, but Agile thrives on collaboration and feedback, adjusting and evolving as the customer’s needs do.
4. Responding To Change Over Following a Plan
Does it throw you off-kilter when you must adapt your work to ever-evolving circumstances? Agile’s fluid nature shines here, accommodating change rather than stubbornly clinging to an outdated plan. This is where agile project management really separates itself from the pack, and agile project management tools can help you better respond to these changes.
The 12 Agile Project Management Principles
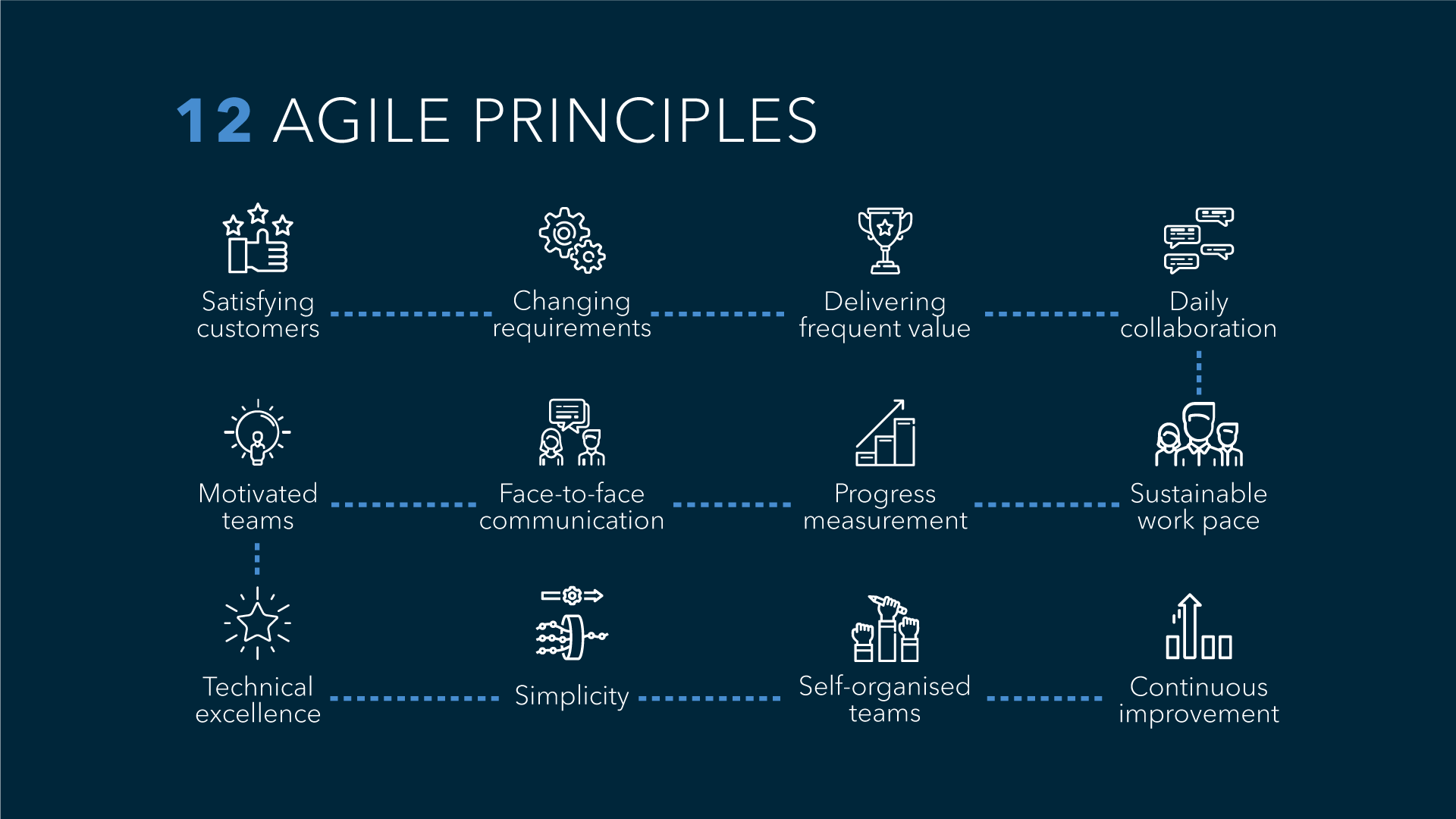
After shedding light on the four core values of Agile, it’s time to delve deeper and unveil the 12 principles of Agile project management. These principles stand as the backbone of this revolutionary methodology and are significantly shaping how businesses orchestrate their projects.
- Highest Priority: The first and foremost principle preaching that customer satisfaction is achieved via continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Welcome Change: Embrace change even late in development for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Frequent Delivery: Deliver working software frequently, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Collaboration: Business people and developers must work together regularly throughout the project.
- Motivated Individuals: Crafting an environment where motivated individuals can work to their best.
- Face-to-Face Conversation: An efficient way of conveying information.
- Primary Measure: Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Sustainable Pace: Agile processes promote sustainable development at a constant pace.
- Excellence: Attention to technical detail and design enhances agility.
- Simplicity: Maximizing the amount of work not done—is essential.
- Self-Organizing Teams: The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- Iterative Approach: Regular reflection and adjustment to behavior are integral components of the Agile approach.
Agile Project Management Frameworks and Its Methodologies
Agile project management is a unique framework that breaks projects down into dynamic phases, often called sprints. This is not only a framework but also a well-fledged methodology. Importantly, this project management, though highly effective for software teams, isn’t limited to just this industry. Regardless of your team’s field, you can harness this dynamic methodology for continuous improvement.
While Agile project management is the overarching approach, within it, you’ll find different methodologies and frameworks that resonate with Agile’s core principles. These Agile project management frameworks provide guidance and best practices; they also allow room for adaptations to fit your project needs. Management frameworks can be viewed as a flexible subset of project management methodologies, enabling you to use the rules and practices in the most suitable way for your project.
One popular framework, known as Kanban, was founded on the Japanese concept of a visual card. The Kanban framework is a user-friendly approach with a card-like layout symbolizing each task within a project. Projects are categorized into three sections namely: ‘to do’, ‘in progress’, and ‘completed’. Thus, as tasks reach milestones, they transition under the category that reflects their current status. Just like your Agile project management tools do, the Kanban board aids in visualizing workflow and task progress, thereby fostering transparency and productivity.
Pros & Cons of Agile Project Management
When it comes to Agile project management, it’s crucial to analyze the benefits and potential drawbacks it can present for your business. Analyzing these allows you to get the best out of Agile and objectify any limitations.
Pros
- One of the significant advantages is flexibility.
- Agile teams have the capacity to shift project focus swiftly
- It is an adaptable choice for quick-paced teams.
- Agile hones the attribute of collaboration within the team.
- Team collaboration is the backbone of Agile.
- It can enhance communication and lead to better project execution.
- Agile is renowned for faster product outcomes.
- The methodology prioritizes delivering working aspects over striving for perfection.
Cons
- Agile projects are prone to scope creep.
- They have less rigid expectations for outcomes that can sometimes cause teams to lose focus.
- Predictability is considerably lower, which can lead to several project-threatening issues
- With more flexibility, generally comes less rigid planning, and this may often result in extended project timelines.
Conclusion
By now, you’ve grasped the essence of Agile project management. It’s not just about software or tools; it’s about a mindset. A mindset that thrives on customer satisfaction, flexibility, frequent delivery, and collaboration. It’s about empowering your team, fostering effective communication, and striving for technical excellence. It’s about keeping it simple, allowing for self-organization, and continually learning and improving. All these principles are the driving force behind Agile’s success. So, it’s time to embrace Agile. Take these principles to heart and let them guide your project operations. You’ll soon see the difference Agile can make. It’s not just a methodology, it’s a game-changer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is Agile approach in project management?
Agile project management is an iterative methodology that focuses on delivering software progressively through various project stages. It encourages continuous feedback and adaptation to changes in user requirements to improve software quality and performance.
Q2. What are the guiding principles of Agile project management?
The guiding principles of Agile project management encompass customer satisfaction through early software delivery, flexibility toward changing requirements, regular delivery of functional software, collaboration between businessmen and developers, supporting a motivated team, effective communication, continuous development, maintaining technical excellence, simplicity, self-organization, and continual improvement.
Q3. What are the 5 phases of Agile project management?
The 5 phases of Agile project management include:
- Envision Phase: Initial project visioning and planning.
- Speculate Phase: Developing a progressive feature-based plan.
- Explore Phase: Iterative cycles of product development and testing.
- Adapt Phase: Review and refine the project.
- Close Phase: Finalizing and ending the project.
Q4. What is agile project life cycle?
The agile project life cycle is a series of systematic stages a project goes through, from initiation to completion. The stages include concept, inception, iteration, release, maintenance, and retirement.
Q5. What are the 4 principles of Agile?
The four main principles of Agile include favoring individuals and interaction over processes and tools, valuing working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and being more responsive to changes than strictly sticking to a plan.
Q6. What is Agile vs Scrum in project management?
Both Agile and Scrum are iterative frameworks for project management. Agile focuses on providing software progressively with continuous user feedback and adjustments, which works best for smaller teams and simple design. Scrum, on the other hand, completes software delivery after each sprint. It suits more creative, experimental approaches.

Leave a Reply