Best Strategies To Boost Your Schedule Performance Index In 2024
Imagine you’re in charge of a major project, and you need a reliable way to gauge its progress. That’s where the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) comes in. It’s a handy tool that helps project managers like me keep a pulse on our project’s health, giving us a clear picture of how efficiently we’re using our time and resources.
In essence, SPI is a ratio that tells us if we’re ahead, on track, or behind schedule. It’s a simple yet powerful metric that can make or break a project’s success. So, whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just starting in the field, understanding SPI can be a game-changer. Join me as we delve deeper into this vital project management tool.
Understanding the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)

Here, we will have an understanding of the Schedule Performance Index. What it means, how important it is for project management, and much more. Let’s just have a look.
What Is the Schedule Performance Index
The Schedule Performance Index, commonly referred to as SPI, acts as an efficiency measure. SPI, calculated as the ratio of earned value to planned value, provides a numerical indication of the status of a project. Values exceeding 1 suggest that the project runs ahead of the planned schedule, whereas values less than 1 normally indicate a project lagging behind schedule. For instance, an SPI value of 0.90 signifies that only 90% of the planned work has swiftly been completed.
The Importance of Monitoring Project Performance
Monitoring project performance doesn’t simply spring up as an essential chore; it’s vital for successful project completion. So, you should know the risk assessment matrix.
Utilizing indices such as SPI allows project managers to simplify their evaluation process, by offering a precise, numerical representation of project progress. SPI in particular helps identify bottlenecks, promoting timely interventions which, in turn, mitigate excessive resource consumption and delay in completion.
By accurately evaluating project performance, managers pave the path for effective decision making. They are equipped with pointers for performance adjustments, if and when necessary, reducing the chances of unforeseen hurdles down the line. For example, an SPI of 0.75 may prompt the redirection of resources to meet deadlines, reinforcing the essence of timely monitoring in averting potential setbacks.
Calculating the Schedule Performance Index
To delve deeper into the intricacies of Schedule Performance Index (SPI), understanding its calculation becomes crucial. It’s a quantitative process, grounded in a simple yet insightful formula.
The Formula Explained
The nucleus of SPI calculation is a ratio. It’s expressed as the division of the Earned Value (EV) by the Planned Value (PV). Simply put, SPI equals EV divided by PV, or SPI = EV/PV. Both EV and PV are essential elements in project management.
Earned Value (EV), often termed Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP), represents the value of accomplished work up to a certain point in time. Meanwhile, Planned Value (PV), or Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS), symbolizes the allocated budget for specified work until a specific period.
This ratio provides professionals with rich insights into the project’s progress.
Example Calculation of Schedule Performance Index
Let’s illustrate the Schedule Performance Index calculation process using an example. If a project has a Planned Value (PV) of $200,000 for work scheduled within a specific timeframe, and the Earned Value (EV) from work performed during this period is $175,000, then:
SPI = EV / PV
SPI = $175,000 / $200,000
By computing this, one gets an SPI of 0.875. This value, being less than 1, indicates a project falling behind schedule. Conversely, an SPI greater than 1 signifies a project is running ahead of its planned schedule, while an SPI equal to 1 demonstrates the project is on schedule.
Remember, the value of SPI guides timely interventions, allowing effective decision-making, and preventing unnecessary wastages. Hence, its regular computation is an essential practice for successful project management, like operational readiness.
Interpreting the Schedule Performance Index
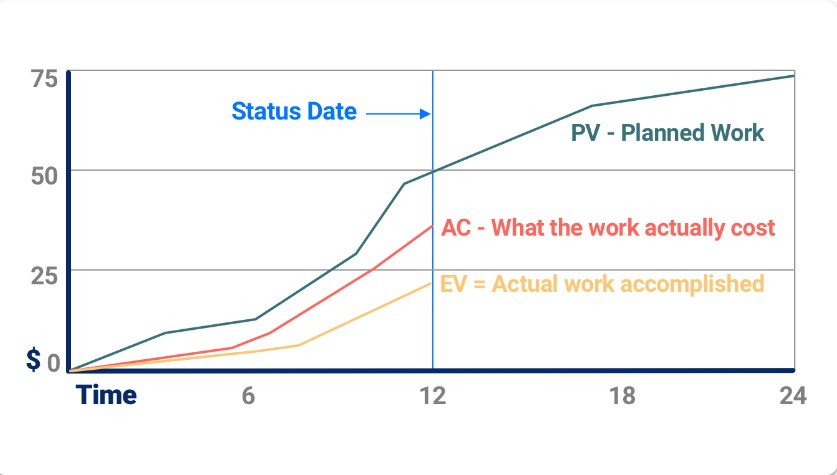
Interpreting the Schedule Performance Index, or SPI, offers valuable insights into the health of a project. By delving into the details of SPI figures, project managers gain the ability to make informed decisions. This understanding of SPI interpretation assists in identifying potential issues early and taking immediate action.
What Does an SPI Greater Than 1 Indicate?
An SPI greater than 1 offers a positive indication in the context of project timelines. It signifies that work is progressing at a faster pace than planned. Let’s consider an SPI of 1.2, for instance. In this scenario, earned value surpasses the planned value by 20%. However, don’t mistake a higher SPI as an indicator of cost efficiency. High SPI merely suggests better time resource utilization, not cost-effectiveness.
What Does an SPI Less Than 1 Mean?
On the contrary, an SPI less than 1 signals potential concern: the project lags behind the schedule. For example, an SPI of 0.8 shows that only 80% of the planned project work has been completed. Despite this red flag, remember not to panic. Instead, use these insights to analyze issues, identify underlying causes, and devise appropriate solutions to get back on track.
Schedule Performance Index and Project Health
Schedule Performance Index is a potent determinant of project health and should be regularly monitored. With an SPI of 1, the project is right on schedule, striking the perfect balance between expectations and reality. However, noting the Schedule Performance Index alone isn’t sufficient. Consider other performance metrics, such as the Cost Performance Index (CPI), to gain a comprehensive understanding of the project’s overall health.
I encourage project managers to use SPI to maintain an eagle-eye view of their projects, identifying potential hiccups, and implementing effective corrective measures to ensure successful project execution and timely completion.
Integrating SPI Into Project Management Practices

My job here is to dive deeper into how Schedule Performance Index gets integrated into project management practices.
Setting Up Effective Baselines
Project baselines establish a yardstick against which SPI gets measured. The establishment of solid baselines is crucial, and they often form the foundation of SPI calculation. Including pivotal project parameters like cost, schedule, and scope in these baselines can lead to a more comprehensive Schedule Performance Index interpretation.
In essence, a baseline reflects the original project plan. An effective baseline captures the project’s scope in terms of deliverables and objectives, the project timeline detailing start and finish dates of tasks, and the outlined project budget.
To illustrate, let’s consider a project aiming to develop a new software feature. The deliverables would include both the software feature and the supporting documentation. The timeline might span several sprints or Phases, and the budget might allot resources for development, testing, and documentation personnel. The project baseline would then include these details, allowing SPI to reflect if the project is on track, ahead, or behind schedule accurately.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
SPI’s effectiveness lies mostly in the frequency of its application. Regular monitoring of Schedule Performance Index allows project managers to identify potential scheduling issues early and take corrective action before the problems become significant.
An effective Schedule Performance Index monitoring practice includes periodic calculation typically at the end of every project phase or sprint, comparing the calculated Schedule Performance Index to the set project baseline, and interpreting the resulting value in terms of project performance.
For example, if a project was set to finish a phase within two weeks with an assigned budget, reaching only 75% completion at the end of two weeks would result in an SPI less than 1. This indicates the project is falling behind schedule and requires corrective actions. These could be anything from resource reallocation and additional hiring to process changes and scope reduction. Regular Schedule Performance Index monitoring thus enables project managers to make these adjustments promptly, ensuring the project stays on track and meets its objectives.
Maintaining a project’s health is a dynamic process and incorporating SPI into daily project management practices helps underpin the ever-changing landscape of a project’s progress.
Limitations and Considerations of Schedule Performance Index
The Schedule Performance Index (SPI), provides insights into how efficiently a project is progressing concerning its schedule. However, like any metric, it has its limitations and considerations. Here are some key points to discuss:
External Factors Affecting Schedule Performance Index
In the proper application of Schedule Performance Index, one must not neglect the influence of external factors. These elements, outside the project’s scope, often play a significant part in the actual performance in contrast to the planned value. Various elements such as unpredictable weather for construction projects, shifts in government regulations, market changes like sudden spikes in equipment costs, or unforeseen workforce disruptions become integral considerations.
For example, a planned project in the tech industry foresees a high Schedule Performance Index due to a well-structured plan and optimal resource allocation. But, if there’s a sudden change in market trends or tech regulations, the project might fall behind, causing a drop in Schedule Performance Index. Hence, while Schedule Performance Index holds crucial insights into a project’s temporal efficiency, it doesn’t account for the unpredictability of external factors.
Limitations in Forecasting Project Completion
Just as every coin has two sides, Schedule Performance Index, too, has its drawbacks when it comes to forecasting project completion. Primarily, SPI focuses on the past and present status of a project but struggles to predict the future effectively. Just because a project maintains an SPI greater than 1 does not guarantee its timely completion. Exemplifying, if a project shows an SPI of 1.5 during its initial phase, one can’t confirm that it’ll complete ahead of time, as upcoming tasks might be more complex and time-consuming.
Moreover, SPI fails to capture the true essence of project complexities. Projects composed of intricate and interdependent tasks often get misrepresented by SPI calculations. Herein, SPI might show a high value, providing a false sense of security about the project’s status. For instance, in software development projects, complex programming tasks may take longer than expected, lowering the SPI, even if previous tasks were efficient.
So, it’s essential to understand SPI’s limitations while striving for that optimal schedule performance. Supplementing SPI with other project management tools and continual context consideration facilitates a more accurate view of the project’s progress.
Best Practices for Improving Schedule Performance Index

In the pursuit of improving the Schedule Performance Index (SPI), implementing a series of best practices proves beneficial. Focusing on proactive project planning, effective communication and stakeholder engagement, and utilizing software for schedule tracking can enhance your SPI significantly.
Proactive Project Planning
Proactive project planning lays the groundwork for significant impact on Schedule Performance Index. As a project manager, it’s crucial to generate a robust and realistic schedule during the planning phase. Taking into account the project’s scope, available resources, and potential risks in project management enables creation of a practical timeline. For example, when setting up a project timeline, ensuring contingencies for unforeseen delays minimizes the risk of falling behind schedule, thereby improving SPI.
Additionally, establish baselines for scope, cost, and schedule parameters during project planning. This, in turn, facilitates more precise tracking and control of project progress, paving the way for a more accurate SPI calculation over the duration of the project.
Effective Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders effectively and maintaining open communication pathways represents another pivotal practice to improve SPI. Regular progress update meetings and timely briefings help in keeping everyone on the same page in terms of project status. For instance, discussing the SPI during stakeholder meetings ensures everyone understands if the project is ahead or behind schedule. This transparent sharing of project status often leads to a cooperative approach towards problem-solving, propelling the project towards its schedule targets.
Utilizing Software for Schedule Tracking
In today’s digital age, software solutions for schedule tracking are a must-have tool in a project manager’s arsenal to improve SPI. Prime examples of these solutions include Microsoft Project, Asana, and Trello. These platforms allow automated computation of SPI by inputting Earned Value (EV) and Planned Value (PV) values. The real-time tracking of scheduling deviations empowers project managers to swiftly identify issues and make necessary adjustments. Thus, leveraging such software can streamline project scheduling tasks, resulting in an improved SPI over time.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively using the Schedule Performance Index can make a world of difference in managing your projects. Remember, it’s not just about calculating SPI; it’s about using this valuable metric to steer your project in the right direction. Proactive planning, clear communication, and stakeholder engagement are key to improving your SPI. Additionally, don’t underestimate the power of software tools. They can offer real-time insights and facilitate quick adjustments, keeping your project on track. So, don’t wait! Start putting these best practices into action and watch your SPI improve. After all, a healthy SPI is a clear sign of a project moving smoothly towards its goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is Schedule Performance Index (SPI)?
SPI, or Schedule Performance Index, is a tool used by project managers to effectively monitor the progress of a project. It’s calculated as a ratio of Earned Value (EV) to Planned Value (PV), and different values signify different project progress statuses.
Q2. What does SPI greater or less than 1 signify?
An SPI greater than 1 shows that the project is progressing ahead of its planned schedule. Conversely, if the SPI is less than 1, it indicates that the project is falling behind its intended schedule.
Q3. How can SPI be improved?
Improvement in SPI can be achieved through proactive project planning, effective communication with stakeholders, and leveraging software tools for schedule tracking. These steps ensure accurate progress tracking, better problem-solving approach, and prompt adjustment of scheduling deviations, respectively.
Q4. Why is it important to monitor SPI regularly?
To accurately assess project progress, it’s important to consistently monitor SPI. Regular tracking aids in detecting potential issues early, enabling timely remedial actions, and optimizing project performance.
Q5. What Software Tools are recommended for improving SPI?
Software tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, and Trello are recommended for improving SPI. These tools help in real-time scheduling deviation monitoring, thereby aiding in making prompt adjustments, which can, in turn, enhance SPI over time.

Leave a Reply