Excel in IT Project Management | Best Practices in 2024
It can seem impossible to understand the digital world of IT project management. But, fear not! I’m here to help you traverse this complex terrain. With years of hands-on experience, I’ve got a treasure trove of insights to share.
We’ll explore the ins and outs of IT project management, shedding light on its importance in the tech-driven business world. From planning to execution, we’ll delve into the critical processes that ensure project success. So, buckle up and get ready for an enlightening journey into the world of IT project management.
What Is IT Project Management?

To tread successfully on the technological trails, IT project management offers an effective roadmap. It’s steeped in discipline, focusing on the planning and organization of a company’s resources. Let’s delve into its significance and the basic structures that create a sturdy foundation.
The Importance of Specialized Management in IT
Envision IT project management as a potent bridge connecting technology and business goals. Instead of traditional management forms, IT project management proposes a specialized approach, proficiently grappling with unique challenges like shifting technology landscapes, security issues, and fast-paced changes.
For instance, an IT project manager coordinates team members, like software developers, network engineers, and data analysts, towards the unified achievement of set objectives. They’re tasked with ensuring all parts morph into a well-oiled machine, targeting efficient production, minimization of risks, and optimized returns on the financial and time investments made.
Key Components of IT Project Management
The anatomy of IT project management contains vital elements, each contributing to the effective management of projects from initiation to closure.
- Project Integration Management: The maestro leading the orchestra, it’s responsible for harmonizing all other project aspects. It guides project tasks in alignment with the project charter and plan.
- Scope Management: Defining the project boundaries, it ensures that only relevant tasks, powerful for goal achievement, gain a pass onto the project checklist. For example, during the development of a new software application, scope management oversees what features and functionalities are included.
- Time Management: Every tick of the clock matters in IT project management. This component focuses on detailed project scheduling software, tracking progress, and making adjustments to ensure deadlines aren’t overlooked.
- Cost Management: It’s about number-crunching and budgeting. Balancing quality and cost, it aims to deliver a project that packs a punch but doesn’t drain the wallet.
- Quality Management: This component polishes the final product. It safeguards the quality standards set by ensuring that the project outputs match the initial specifications.
- Communications Management: A project can crumble due to poor communication. A vital component, it ensures efficient information flow among stakeholders and team members.
- Risk Management: It not only identifies potential risks but also devises strategies to lessen their impact. Recognizing potential security threats or project delays, types of risk in project management works to keep the project on track.
Together, these components create a strong, flexible core for IT project management, pushing for project success and competitive advantage. It’s a well-built fort, where every brick is vital and interdependent.
The IT Project Life Cycle
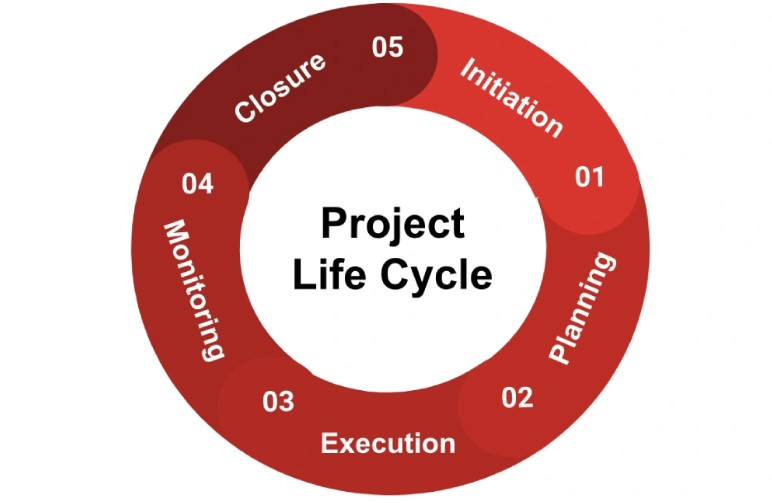
Continuing from the core elements of IT project management, a conversation on the IT project life cycle deserves immediate attention. It’s a crucial sequence that every effective IT project manager follows. Let’s dive into its main steps – Initiation and Planning, Execution and Monitoring, and Closing and Evaluation.
Initiation and Planning
The first two stages, initiation and planning, mark the start of the project cycle. Here, I perform a preliminary analysis to establish the project’s feasibility, defining its main objectives and expected outcomes. I get my team onboard and together, we lay down a strategic plan that serves as our road map. This involves defining clear, actionable tasks, setting achievable schedules and realistic budgets, and developing a risk management plan. Thus, I make sure that every project starts off on the right foot, with a solid foundation of well-defined goals and a clear path to reach them.
Execution and Monitoring
Once the planning phase is complete, we enter the execution and monitoring stages. It’s during these phases that the project plan is actualized and I start to see the fruits of our labor. However, this stage is also challenging as it requires close monitoring to ensure that the project stays on track. Regular status updates, consistent team communication, and constant performance metrics monitoring become my day-to-day routine. If any divergence from the plan occurs, I ensure prompt corrective measures, keeping the team focused and project on schedule.
Closing and Evaluation
The final stages—closing and evaluation—are the culmination of the project life cycle. My tasks range from tying up loose ends to evaluating the project’s performance against predetermined objectives. Reviewing project successes, learning from mistakes, and documenting lessons are key components of this phase. The insights gained here prove invaluable for future projects, helping me improve my management strategies and continually raise the bar on IT project execution excellence.
Altogether, an understanding of the IT Project Life Cycle enables me and my team to streamline our workflow, allocate our resources efficiently and, ultimately, deliver superior project outcomes.
Methodologies in IT Project Management

Translating knowledge of the IT project lifecycle into success, often hinges on the methodology adopted. Varied and unique, each methodology offers a distinctive approach to managing IT projects.
Agile
Agile principles prioritize flexibility, advocating for iterative development. Derived from repetitive software development, Agile breaks tasks down into small increments, with minimal planning involved. Each increment is, in essence, an individual project. Review sessions occur after each iteration, allowing for modifications based on user feedback. Agile prioritizes customer satisfaction, underpinned by timely and continuous delivery of useful software.
Waterfall
Sequential in nature, the Waterfall methodology traces its roots to the construction and manufacturing industries. Unlike Agile, it mostly disregards iterative development. The project progresses steadily downwards (hence, “Waterfall”) through static phases – conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, and maintenance. A phase is only initiated after the successful completion of the preceding one. Rigidity is its hallmark – alterations to the project scope after initiation are complicated, if not impossible. The Waterfall methodology ensures meticulous planning and design but leaves little room for changes.
Scrum
An offshoot of Agile, Scrum excels in rapidly changing or highly emergent environments. The project is divided into small, manageable units known as “sprints” that focus on delivering the most valuable features first. Each sprint lasts for a specified time – typically two weeks. Daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, and retrospectives are core components, allowing for constant feedback. Scrum enhances team-based collaboration while promoting continuous improvement and flexibility.
Embedded in these methodologies – Agile, Waterfall, and Scrum – lies the power to tackle the dynamic challenges of IT project management. The definitive choice hinges on the project’s scope, complexity, and available resources.
Tools and Technologies for IT Project Managers

Let’s dive into a crucial aspect of IT project management – the tools and technologies. These are the lifelines that help managers streamline the work process, engage with the team, and ensure the project’s seamless execution.
Project Management Software Options
I am often asked about the best project management software options. It’s tough to declare one as the clear winner, considering the abundance of options available. However, some stand out due to specific functionalities and widespread acceptance.
For those who love crystal clear progression metrics, Jira is worth considering. It offers highly customizable dashboards, perfect for Agile-based projects. Another popular choice is Microsoft Project software, perfect for scheduling and resource management. Trello’s simplistic approach suits smaller teams, providing cards as a simple, visual way to manage work plan.
On the other hand, Asana excels in task management and Gantt chart visualization, helping teams remain focused and organized. Finally, Basecamp, with its stress-free interface, facilitates effortless collaboration and task delegation.
Remember, the chosen software ought to suit the project’s scope and complexity, along with team preferences and organizational resources.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
The shift towards remote working has highlighted the importance of communication and collaboration tools. They have emerged as a lifeline for project teams.
Slack has become the go-to tool for quick, seamless communication. It supports various integrations with other software, enhancing project flow. For video conferencing, Zoom provides an optimal experience, facilitating virtual meetings with superior sound and video quality. Microsoft Teams combines chat, meetings, and calling into a unified platform, ideal for larger organizations.
For collaboration on documents and files, Google Workspace is invaluable, providing live editing and real-time collaboration. Similarly, Dropbox allows file sharing and storage, ensuring project files are neatly organized.
Communication and collaboration tools are invaluable for project managers, helping bridge the gap between remote team members and ensuring efficient teamwork and teamwork quotes. Note that it’s essential to evaluate personal team dynamics and project requirements when choosing these tools.
Challenges in IT Project Management

While the IT project management landscape can be rewarding and dynamic, it presents several unique challenges. By navigating through these, an organization or team can ensure successful project execution. Here, I’d elaborate on the struggles in handling remote teams and constantly changing technology trends.
Handling Remote Teams
Managing remote teams turns into a major hurdle for many IT project managers. Regardless of the power-packed tools like Slack, Zoom, or Microsoft Teams that exist today, several obstacles persist.
Firstly, time zone differences can impact team collaboration. When team members live in different parts of the world, they’re less likely to be online at the same time. Frequent workshops, meetings, or discussions can thus become a challenge. For instance, a New York-based team may struggle to schedule meetings with colleagues in Sydney.
Secondly, creating a unified company culture becomes increasingly complex with remote teams. Feeling part of a team promotes a sense of belonging, which can boost productivity. However, organizing team-building exercises or creating a shared culture is difficult when team members can’t physically interact.
Thirdly, monitoring productivity is yet another challenge. Although project management tools assist in tracking tasks and deadlines, measuring an employee’s efficiency is less straightforward.
Lastly, resolving conflicts can be tougher. In a physical office space, issues can be identified and addressed immediately. Conversely, online communication may not always be as effective or prompt.
Managing Changing Technology Trends
Staying abreast with ever-changing technology trends poses a constant challenge to IT project managers. Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), BlockChain and 5G networks have significantly impacted IT project management.
For example, integrating AI into project management tools can enhance project efficiency and productivity. However, implementing such technology without disrupting ongoing projects requires careful planning and possible team training.
Similarly, the adoption of IoT devices can streamline process automation but also introduces new security vulnerabilities. This imposes the necessity for IT project managers to comprehend the potential risks and implement effective security measures.
Thus, keeping pace with technology advancements, deciding which trends to adopt, understanding their implications, and training the team accordingly is essential yet quite challenging.
In essence, these challenges underline the need for effective strategies, versatile skill sets, and technology solutions to enable successful IT project management.
The Role of a Project Manager in IT

We know about IT project management, its challenges and everything. Now let’s know about the role of a project manager in IT.
Leadership and Team Management
In IT project management, the project manager plays a pivotal role in leading the team. They channelize their expertise towards facilitating efficient collaboration within the team, skillfully navigating the complexities of remote work, if required. Adept at handling diverse personalities, the project manager promotes an environment of inclusivity and open communication, encouraging the team to share ideas and feedback. Their ability to strategically delegate tasks, taking into account each member’s strengths and weaknesses, often serves as a lifeline to the project’s successful completion. They also have an inherent responsibility to motivate their team, ensuring that they remain committed to their tasks with a shared vision of the project’s goals.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
The IT project manager is intrinsically involved in risk assessment and mitigation at every stage of the project. Brainstorming possible risks, they create contingency plans to tackle potential roadblocks. By using various risk management tools and frameworks, they identify, categorize, prioritize, and strategize ways to control or eliminate risks. It’s not unusual for them to engage in rigorous risk scenario analysis, developing multiple back-up plans to ensure the project’s smooth progression. They bear a crucial role in reassessing risks continuously through the project’s lifecycle, tweaking the risk-mitigation strategies as needed, based on the evolving project dynamics. Further, they effectively communicate these risks to the relevant stakeholders, thus steering the project away from potential pitfalls skillfully.
Metrics and KPIs in IT Project Management

After a comprehensive overview of IT project management essentials and challenges, let’s move into discussing the pivotal role of metrics and KPIs. Project success relies heavily on constant measurement and evaluation. In this age of data, it´s clear that numbers and benchmarks provide the lens through which IT project management gain perspective and make informed decisions.
Tracking Project Success
Plotting the course to success involves particular metrics and KPIs for real-time tracking of the project’s health. I´ve found that keeping an eye on specific gauges, such as project milestones, budget variance, or scope change frequency, offers vital snapshots of the project status.
For example, using project milestones provides adequate checkpoints for progress and keeps everyone aligned. In contrast, budget variance offers insights into financial performance compared to predetermined targets or benchmarks. Another crucial metric, scope change frequency, gives us an understanding of how often project parameters venture beyond agreed boundaries.
Maintaining regular checks on these metrics helps in identifying areas that require immediate attention, rectifying issues early, and ensuring the project stays on course. It’s not only about meeting milestones, controlling costs, or sticking to the project scope, but about comprehending the broader picture of project performance.
Improving IT Project Outcomes
One of the fundamental roles of IT project managers is managing outcomes and driving improvements. When it comes to this, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) become the shining beacon, guiding efforts to enhance IT project results.
Key indicators like Time-to-market (the time taken for a project to go from conception to launch), Return on Investment (ROI), and Customer Satisfaction Index are paramount. With time-to-market, one can measure the project’s efficiency, while ROI provides understanding about the project’s profitability. Meanwhile, customer satisfaction reveals how well the project meets its user’s requirements and expectations.
Incorporating these KPIs allows us to gauge the project’s real success beyond just completion and delivery. It’s about ensuring the project adds value, delights the user, and contributes to the broader strategic objectives.
Remember, metrics and KPIs, when utilized effectively, offer tools for both tracking and improving IT project outcomes. They place us in a better position to steer the project towards success and remain astute to any potential pitfalls in the journey.
Conclusion
I’ve walked you through the ins and outs of IT project management, from methodologies to tools, to the vital role of project managers. We’ve also navigated the challenges that come with managing remote teams and keeping pace with rapidly evolving tech trends. We’ve underscored the importance of versatile skill sets in this dynamic field. But it doesn’t stop there. We’ve delved into the criticality of metrics and KPIs, emphasizing that constant measurement and evaluation aren’t just nice-to-haves, but must-haves. And let’s not forget the role of specific metrics and KPIs in driving improvements and gauging success. It’s clear that IT project management isn’t just about getting the job done – it’s about strategic impact and value. So, here’s to the power of IT project management, a critical piece of the business puzzle that’s set to shape the future of work.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the importance of IT project management?
IT project management is important as it ensures the successful completion of IT projects within the stipulated timeline and budget. It efficiently manages resources, mitigates risks, and oversees the IT project lifecycle stages.
Q2. What are some popular methodologies used in IT project management?
Popular methodologies include Agile, Waterfall, and Scrum. Agile promotes continuous iterations, Scrum implements Agile principles in a specific manner while Waterfall follows a sequential model.
Q3. What tools and platforms can enhance IT project efficiency and remote teamwork?
Jira, Microsoft Project, Slack, and Zoom can enhance IT project efficiency. They facilitate better remote team collaboration, project tracking, and communication.
Q4. What are some challenges faced in IT project management?
Managing remote teams, adapting to quickly evolving technology trends such as AI and IoT, and the demand for versatile skill sets in IT project managers are noteworthy challenges.
Q5. How do project managers play a pivotal role in IT Projects?
Project managers are central to IT projects as they lead team management, ensure the completion of project milestones, handle risk assessment, and implement mitigation strategies.
Q6. How significant are metrics and KPIs in IT project management?
Metrics and KPIs like project milestones, budget variance, Time-to-Market, ROI, and Customer Satisfaction Index play a critical role in tracking project status, driving improvements, and evaluating project success beyond completion.

Leave a Reply