Effective Monitoring and Controlling in Project Management
Navigating the complex waters of project management can feel like steering a ship in a storm. Among the most crucial components of this journey are monitoring and controlling. They’re not just buzzwords, they’re the compass and rudder that guide a project to its destination.
In the intricate maze of project management, it’s easy to lose sight of the end goal. That’s where monitoring and controlling step in. They keep you on track, ensuring you’re not drifting off course.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into these vital aspects of project management. We’ll explore their importance, how they work, and why any successful project manager should have them in their toolkit. Let’s set sail on this enlightening journey together.
The Importance of Monitoring and Controlling in Project Management

Just as a compass and rudder guide a ship to its destination, monitoring and controlling steer the course of a project. These two components form the backbone of project management, acting as safeguarding mechanisms that stop a project from getting off its intended path.
Why Monitoring Is Critical to Project Success
‘Prevention,’ as they say, ‘is better than cure.’ Monitoring identifies obstacles early on, essentially preventing the proverbial boat from sinking. It’s a proactive approach that starts at the inception of a project and continues until its culmination.
Below are the reasons why monitoring is critical to project success:
- Unforeseen Challenges: Monitoring helps to spot unforeseen challenges that might arise during a project. An example includes sudden changes in the market conditions that might affect the business strategy.
- Timely Corrections: Early detection of issues allows for timely corrections, preventing minor problems from becoming significant issues. For instance, if the team is consistently missing deadlines, corrective actions can be implemented immediately.
- Communication: Monitoring provides frequent updates, informing all stakeholders about the project’s progress. After each monitoring activity, a report detailing the project’s status gets distributed, improving transparency and communication.
How Controlling Processes Influence Project Outcomes
While monitoring relates to tracking, controlling focuses on taking corrective actions. Once an issue is identified through monitoring, controlling processes swoop in to rectify the situation. They ensure that the project stays aligned with its established objectives.
Here are ways how controlling processes influence project outcomes:
- Resource optimization: Controlling processes help manage resources more efficiently. For instance, if a task is ahead of schedule, resources assigned to it can be reallocated to other tasks lagging behind.
- Quality maintenance: Controlling ensures that the project remains within its specified quality standards. If a product’s quality begins to wane, controlling processes like quality checks trigger to bring it back on track.
- Risk mitigation: With controlling processes, potential risks can be mitigated. If there is a high risk of a supplier failing to deliver, backup suppliers can be arranged in advance to ensure a smooth project flow.
Remember, effective monitoring and controlling can mean the difference between the success and failure of your project. They are the force fields that protect your project from external and internal uncertainties, ensuring its steady journey towards the set goals.
Key Components of Monitoring in Project Management
Monitoring constitutes a pivotal aspect of project management, contributing to project success by enabling the timely identification and rectification of issues. This section elucidates upon two main components of monitoring in project management – the establishment of performance metrics and the implementation of effective tools and techniques.
Establishing Performance Metrics
The first step in project monitoring often revolves around establishing performance metrics. These are specific, measurable values that serve as indicators of the project’s overall health and performance. They provide a quick, clear snapshot of where the project stands at any given moment. I use them to track progress and performance, align team efforts, and foresee potential risks.
Take, for example, the Earned Value Management (EVM) system. EVM is a quantitative project management tool that objectively measures project performance in terms of scope, cost, and time. It effectively integrates three vital areas of project management, assisting in overall project performance evaluation and forecasting. This technique utilizes crucial performance metrics like Schedule Performance Index (SPI) and Cost Performance Index (CPI) to provide insight into the project’s current position and future directions.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Monitoring
Implementing efficient tools and techniques forms the second key component of project monitoring. They facilitate data collection, visualization, communication, and decision-making processes within the project. Harnessing the power of technology and specific techniques, I can gauge project performance with greater accuracy and make informed decisions.
Take a project management software like Microsoft Project, for instance. It’s an interactive tool that offers real-time tracking of various project aspects, including task completion, resource usage, and timeline progress. The software allows easy visualization of the project’s performance and generates helpful reports, aiding in making data-driven decisions.
Another noteworthy tool is the Gantt Chart, a visual representation that outlines a project’s scheduled tasks against its timeline. It aids in tracking project progress and highlighting dependencies between tasks, proving incredibly beneficial in maintaining project schedules and identifying potential bottlenecks.
By integrating the appropriate tools and techniques with well-established performance metrics, a robust monitoring process can successfully maintain a project’s progress in alignment with its objectives. This in-depth understanding of project status critically supports swift decision-making and corrective actions, contributing significantly towards overall project success.
Understanding the Control Aspect in Project Management
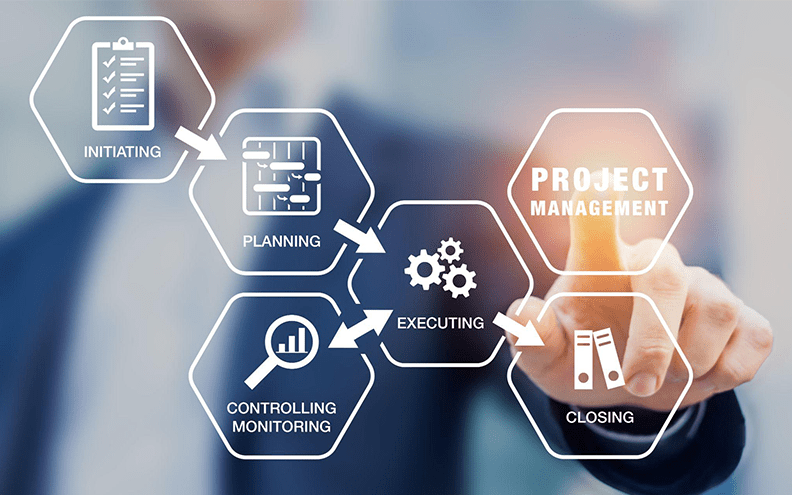
My deep dive into the control aspect of project management begins with a look at one of its essential components: change control mechanisms.
Change Control Mechanisms
Change is inevitable in any project. Hence, project management employs specific change control mechanisms for agile response and adaptation. These mechanisms typically consist of formal procedures and tools that help in assessing, recording, evaluating, and approving or rejecting changes based on their impact on the project’s objectives and constraints.
- Change Request Process, the initial step in change control mechanisms, handles proposed changes. It’s a streamlined process to log, track, and communicate changes, ensuring no request gets lost in the shuffle.
- Impact Analysis, done once a change request gets logged, evaluates how the proposed change will affect the project timeline, resources, and objectives.
- Change Control Board (CCB), a group of project stakeholders, reviews and approves or rejects the change requests. The CCB considers the impact analysis results and the strategic alignment of the proposed change.
For example, a project manager might use project management software, such as Asana or Trello, to log and track change requests. These tools also provide a centralized platform for conducting impact analysis and facilitating CCB meetings, thereby maintaining uninterrupted workflow.
Risk Management and Issue Resolution
Another critical facet of project control is risk management and issue resolution. Predicting future uncertainties and having a plan to mitigate them is integral to project management. As part of risk management, identification of potential risks and creation of detailed plans to handle any issues that might arise during a project execution is crucial.
- Risk Identification forms the foundation of risk management. It involves pinpointing any potential hazards that might derail a project or increase its cost.
- Risk Assessment then analyses the identified risks to understand their potential impact. By ranking risks based on their likelihood and impact, you delegate your resources in the most strategic way.
- Risk Response Planning involves developing action plans to counteract potential risks. Reaction strategies could be avoiding, mitigating, transferring, or accepting the risks.
- Issue Resolution is a proactive approach that addresses any dug-in problems that arise during project execution. It’s a process that takes potential solutions, analyzes them, and applies the most effective resolutions to keep projects on track.
A concrete example of this can be Project Risk Analysis Software such as @RISK or RiskyProject. These solutions aid in identifying and analyzing project risks, and they facilitate the development of detailed risk response plans. Thus, they serve as invaluable tools for risk management and issue resolution.
The Role of Project Management Software in Monitoring and Controlling

Project Management Software (PMS), often plays a crucial role in the efficient monitoring and controlling of projects. Leveraging advanced metrics and visual status indicators, PMS allows for meticulous tracking of project expectations: scope, schedule, and budget.
Automating the Monitoring Process
Monitoring projects can be a daunting task, particularly with large, complex projects involving numerous resources and dependencies. Thankfully, PMS comes to the rescue with automation capabilities. This allows me to set up dashboards and receive auto-generated progress reports, instead of manually tracking each parameter. With software like Microsoft Project or Asana, I can keep a constant eye on the project’s scope, quality, schedule, and costs, automating the monitoring process.
For example, consider a software development project with tight deadlines and heavy workload. With an automated monitoring system, tasks progress gets automatically updated on the system by the team member responsible. In real-time, I notice discrepancies, potential roadblocks or delay indicators. Without such a system, capturing this data alone represents a marathon task.
Streamlining Control Activities with Software Solutions
Software solutions in project management don’t only aid in monitoring but play a pivotal role towards streamlining control activities too. For control activities to be effective, I rely heavily on precise data capture and efficient analysis tools. Tools like Oracle Primavera or Jira provide dashboards for real-time control activities, benchmarking of project status against the baseline, and facilitating corrective actions when necessary. Potential deviations get highlighted, enabling me to act proactively to prevent project derailment.
Concrete instances occur in many IT upgrade projects. At face, they often appear straightforward, but digging under the surface reveals potentially misaligned resources, escalating costs, or under-estimated timelines. All these, if not identified at an early stage, could spell disaster. Having the dashboard indicators from my control software, I garner early insights into these key parameters, facilitating prompt corrective actions.
The role of project management software in monitoring and controlling is pivotal to project success. It not only automates the grueling task of project monitoring but also aids in streamlining control activities by providing real-time data and insights. Factoring in the complexity and scale of modern-day projects, the value of such software continues to amplify.
Best Practices for Implementing Monitoring and Controlling Processes

Injecting effective monitoring and controlling practices into project management is crucial for project success. Here, I’m going to delve into some of the best practices. The focus is on conducting regular progress reviews and adjustments and fostering team communication and collaboration.
Regular Progress Reviews and Adjustments
Routine assessment of progress is instrumental in keeping a project on track. Conduct such reviews by observing parameters such as time, cost, and scope change. It’s beneficial to hold these reviews at prescribed intervals, typically on a weekly or bi-weekly basis.
For instance, use project management software like Microsoft Project to structure your review meetings. The software generates detailed project management reports. You’re able to complete on-demand reports tracking key metrics like resource allocation and task completion.
In adjustments, react promptly to deviations or anomalies. It’s prime when you rectify issues before they escalate. Tools like Asana can assist in this process by sending immediate alerts during fluctuations in the project’s standards.
Fostering Team Communication and Collaboration
Strong communication and collaboration among team members can act as a catalyst for project success. It’s essential to have an open communication channel and foster a collaborative environment.
Take, for example, tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams which streamline communication. You’re able to organize conversations by topic, creating an efficient workflow and ease of information retrieval.
In the collaboration sphere, tools like Trello come to the fore. You’re able to manage collaborative tasks, assign responsibilities, and track progress smoothly. Keeping everyone on the same page eradicates confusion, enhances productivity, and allows for swift accomplishment of project goals.
These best practices are by no means exhaustive, but they certainly form the cornerstone in implementing an effective monitoring and controlling process.
Conclusion
So, it’s clear that monitoring and controlling are vital components in project management. They’re the backbone that keeps a project on track and ensures its success. With tools like EVM and PMS, it’s easier than ever to track progress and resolve issues. And let’s not forget the importance of regular reviews, necessary adjustments, and team communication. It’s these elements that foster a collaborative environment, leading to efficient project management. Whether you’re using Microsoft Project, Asana, Slack, Teams, or Trello, remember it’s the open communication channels and collaborative environments that truly drive project success. So, don’t overlook the power of effective monitoring and controlling in your projects. They’re not just processes, they’re the key to unlocking project success.
Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)
What is the significance of monitoring and controlling in project management?
Monitoring and controlling in project management are essential to track progress, identify potential risks, and resolve issues promptly, ensuring that the project is on track to meet its objectives successfully.
What role does Project Management Software (PMS) play in monitoring and controlling processes?
PMS tools help automate tasks such as setting up dashboards, receiving progress reports, and tracking project parameters, providing a comprehensive view of the project’s health, and enabling faster decision making.
What are some best practices for implementing monitoring and controlling processes?
Best practices include conducting regular progress reviews, making necessary adjustments in real-time, ensuring high-quality team communication, and fostering a collaborative environment.
Which tools are recommended for efficient project management?
Microsoft Project, Asana, Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Trello are some suggested tools that offer functionalities to streamline task distribution, progress tracking, and communication within the project team.
How important is open communication in project management?
Open communication is critical as it facilitates the sharing of project information, problem-solving, and collaboration, ensuring that each team member is aligned with the project objectives and aware of their responsibilities.

Leave a Reply