Project Status Report Template Guide | Optimize Communication
In the bustling world of project management, it’s easy to lose track of where things stand. That’s where the savior of many project managers – the Project status report template – steps in. This unsung hero can simplify your life, streamline your work, and ensure everyone’s on the same page.
But what exactly is a Project status report template, and why should you care? Well, stick around. I’m going to delve into the nitty-gritty of this crucial tool, shedding light on its importance, how it functions, and why it’s a must-have in your project management arsenal. So, whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just starting, there’s something for everyone.
What Is The Project Status Report?

Project status report templates represent a vital cog in the machinery of project management. They serve as a powerful dashboard, converging different strands of a project into a neat, digestible package. This section explores the purpose behind these templates and uncovers the core components that make them tick.
The Purpose of a Project Status Report
A Project Status Report acts as a centralized hub for all project-related information. It conveys a snapshot of a project’s progress, offering team members, directors, and clients a summary of how the project fares.
Managers utilize these reports to track the project’s health, identifying any varied instances from the original project plan. Problems that sneak in, like potential budget overruns or schedule slippages, are promptly flagged and attended to. They’re a version of a health report, but for your projects.
- Project Summary: This area encapsulates the project’s overview, its objectives, the value it intends to deliver, and the current phase it’s navigating.
- Timeline: Presents the project’s timeline, including start and end dates, denoting significant milestones and their respective completion status.
- Tasks: Illustrates a detailed task breakdown, spotlighting the responsible team members and the progress made on each individual task.
- Risks and Issues: Highlights all impending risks and potential issues that could derail the project, along with suitable mitigation strategies.
- Budget: Details the project’s financial aspects, pinpointing all costs incurred, predicted expenditure, and existing financial constraints.
- Key Takeaways and Next Steps: Round up the report, this final component outlines the important learnings from the current status and maps out the imminent steps for the project.
Each component within the project status report should arrive with a precise status tag, such as ‘On Target,’ ‘At Risk,’ or ‘Off Track,’ providing a quick visual reference to the project’s health at a glance.
Choosing the Right Project Status Report Template

Embarking on the quest of choosing the optimal project status report template isn’t always straightforward. It’s crucial to distill specific criteria that these templates must meet, ensuring they meet your project, team, and organizational needs. Further, leveraging some best practices for template customization can exponentially elevate the utility of these templates.
Criteria for Selecting a Template
- Simplicity: A worthwhile project status report template exhibits simplicity, making it understandable to everyone on the team. A simplified template, absent of excessive jargon or convoluted metaphors, fosters comprehension across all team members, regardless of their background or role in the project.
- Flexibility: The selected report template must furnish flexibility. All projects aren’t cloned copies; they encompass dynamic parameters. A template that can adapt to various project types (for instance, agile, iterative, or sequential projects) escalates its usefulness.
- Inclusivity: The template should satisfactorily capture all key aspects of the project, from project summary to timeline, tasks, risks and issues, budget, and key takeaways. A comprehensive template obliterates the need for siphoning information from multiple sources.
- Automation Compatibility: The fourth criterion is automation compatibility. In an era where technology abounds, templates that are compatible with automation software are valuable assets. Automation enhances consistency and significantly reduces manual labor involved in mundane tasks.
Best Practices for Template Customization
While selecting a template is crucial, customizing it to cater to your distinct needs makes it uniquely suitable. Here are a few best practices I employ when customizing a project status report template.
- Tailor to Audience: Modify your template to mirror your audience’s needs. Catering to stakeholders’ needs, ensuring they’re privy to relevant information, establishes active engagement. For instance, if stakeholder emphasis is on budget and timeline, these sections ought to be prominent in the template.
- Incorporate Visual Aids: Embedding visuals like charts, graphs, or progress bars can make data interpretation considerably effortless. Aiding stakeholders visually comprehend project status can be instrumental in avoiding miscommunication and misunderstanding.
- Lean Towards Brevity: Endeavor to curate an uncluttered, concise template. Distill the essence of project status into substantial bite-sized chunks, rather than bombarding stakeholders with detailed narratives.
- Regular Updates: Consistent updates are crucial to maintaining the relevance of a project status report. Customize your template to embed updating cycles, ensuring stakeholders possess the latest and most accurate information regarding the project.
Anatomy of an Effective Project Status Report Template
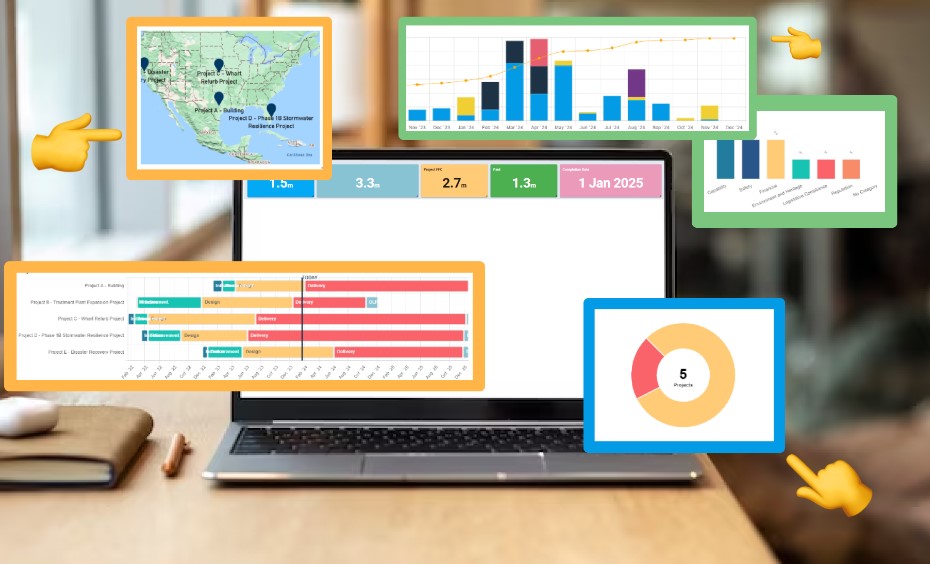
Having previously examined the purpose and best practices for project status report templates, it’s logical to delve into the main sections that constitute them.
Section for Project Milestones
Project milestones, highly significant markers within the timeline, find their place in a dedicated section. It serves as a snapshot of the key achievements or events, offering an instant overview of what’s been achieved so far and what lies ahead. For example, if developing an app, milestones could include Design Completed, Beta Version Released, or Final App Launched. These create a narrative of progress, keeping high-level stakeholders informed and project teams accountable for their objectives.
Financial Summary Area
A well-constructed template features a section summarizing the financial status of the project. Here, budget allocations, cost incurred, forecast expenditure, and variance from the original budget get accurately documented. Think of it as a mirror reflecting the project’s economic health, providing a financial snapshot to help managers make informed decisions. For instance, a surge in unexpected costs could trigger budget revisions or additional funding requests.
Risk and Issues Tracking
No project occurs without risk, hence the requirement for a segment focusing on risk and issue tracking. This section highlights identified risks and challenges affecting the project, capturing their nature, severity, potential impact, and the mitigation strategy. For example, potential risks for an app development project could be timeline delays, technical glitches, or changes in market demand. This tracking ensures a proactive approach to potential hazards before they escalate into serious problems.
Progress and Next Steps
Finally, a project status report template needs a section detailing overall progress and next actions. It accounts for completed tasks, work-in-progress, and upcoming activities, setting the stage for future operations. For example, the “Progress and Next Steps” for an app development project could span from coding to marketing the app. It serves as a roadmap, guiding everyone on the project towards their roles and responsibilities in future tasks. With clarity in ‘where we are’ and ‘where we ought to be,’ project execution becomes a more manageable endeavor.
Implementing the Template in Your Project Management

In light of our discussion about effective project status report templates, it’s crucial now to address their implementation in project management. Integrating these templates with project management tools and training team members in their use are vital steps in this process.
Integrating With Project Management Tools
Integration with project management tools presents a seamless way to implement project status report templates. Project management software like Asana, JIRA, or Trello, for instance, offer functionalities that readily support these templates. In the template context, I feed project data into these tools. Consequently, you see updated project milestones, financial summary, risk, and issues tracking, and progress and next steps accurately reflected. And yes, the more comprehensive the tool, the easier it is to monitor project parameters and thereby utilize the template effectively.
Training Team Members on the Template
Training team members on the project status report template is as mission-critical as integrating it with project management tools. I find it favorable to organize a dedicated workshop or training session to get the team familiar with the template. In the session, I explain the significance of each section – Project Milestones, Financial Summary, Risk and Issues Tracking, and Progress and Next Steps, as examples, their role in project management, and how to update them throughout the project’s lifecycle. Remember, the template serves its purpose only when the team understands its structure and appropriately uses its features to monitor and report project progress.
Examples of Project Status Report Template

Building on the utility and implementation strategies of project status report templates, let’s now delve into some specific instances. Below, I’ll provide a clear snapshot of diverse template examples which are tailored for Agile and Waterfall projects. Additionally, I’ll shed light on the value of industry-specific templates.
Templates for Agile Projects
When considering Agile projects, these evolve rapidly over time. A dynamic template that captures the frequent changes stands as a right fit. An Agile project management report template usually leverages visual elements such as burndown charts, velocity charts, and cumulative flow diagrams for clarity. For instance, the “Agile Scrum Status Report Template” presents project status through sprints, helping teams to efficiently navigate short-term objectives while keeping an eye on the overarching project goals.
Templates for Waterfall Projects
In contrast, Waterfall projects call for a more detailed and focused template. Traditionally, these projects follow a sequential process, and each phase depends on the deliverables of the previous one. So a Waterfall project status report template lays emphasis on a task’s current state, impending risks, and tracked issues. One commonly used template in this scenario is the “Classic Project Management Status Report Template.” It provides a project summary, completed tasks, ongoing work, upcoming tasks, risks and issues, resources used, and financial status.
Industry-Specific Templates
Certain industries necessitate a specialized approach when it comes to reporting project status. Hence, industry-specific templates emerge with relevant sections or data points that cater to the particular needs of an industry. For example, a “Construction Quality Control” often includes sections on site conditions and safety protocols beyond the general reportage of tasks and timeline. Similarly, the “IT Project Status Report Template” puts greater emphasis on technical dependencies, stages of software testing, and bug tracking. These examples showcase the flexibility of project status report templates in addressing unique industry needs.
Measuring the Impact of Your Project Status Report

Having established the role and versatility of project status report templates, we now turn our attention to assessing their impact. The ultimate aim of these templates is to improve project management, which brings up the crucial question: How do you measure the effectiveness of your project status report?
Evaluating Report Effectiveness
Measuring a report’s effectiveness involves analyzing specific outcome metrics. Accuracy plays a pivotal role, reflecting the template’s ability to mirror project reality. Inaccuracy breeds mistrust, impeding communication and decision-making. Nevertheless, a high degree of accuracy maintains trust, aligning stakeholders and team members. Another dimension is comprehensibility. If a report is too complex or too oversimplified, it fails its purpose. Striking a balance, through a clear, concise summary and detailed sections when necessary, fosters understanding.
Let’s not leave out timeliness. Reports need to reflect the current state of the project. Stale information hinders decision-making. Strict adherence to update schedules bolsters both accuracy and relevance, ensuring the report serves as a dependable tool for stakeholders.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Remember, no template is perfect from the get-go. Improvement comes from iteration, typically driven by feedback. Encourage team members, stakeholders, and anyone interacting with the report to provide input. Feedback unveils otherwise unnoticed issues, as well as aspects doing well.
Taking this on board, you make amendments where necessary. Stay open to altering sections or adjusting visual elements, ensuring everyone comprehends the data. Additionally, keep an eye on the industry standards. Innovations often bring about more efficient ways of capturing and reporting data. By remaining ready to adjust your template accordingly, you keep it up-to-date and relevant.
Stay patient, though, as these improvements may not happen overnight. By consistently implementing feedback and revising your templates, you’ll create a productive tool that continues to facilitate successful project management.
Conclusion
It’s clear that project status report templates are invaluable tools in project management. They’re not just about simplifying tasks but also about ensuring alignment within the team. Whether you’re handling Agile, Waterfall, or industry-specific projects, there’s a template designed to meet your needs. But remember, it’s not just about using these templates. It’s about using them effectively. Accuracy, comprehensibility, and timeliness are key factors to consider when evaluating the impact of your reports. And don’t forget the importance of feedback and continuous improvement. They’re essential for refining your templates over time, making them better tools for serving stakeholders and facilitating successful project management. So, if you’ve not yet incorporated these templates into your project management, it’s high time you did. They’ll make your life easier and your projects more successful.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the role of project status report templates in project management?
Project status report templates play a critical role in project management by simplifying tasks and ensuring team alignment. They offer a centralized overview of a project’s progress.
Q2. What types of project status report templates have been highlighted?
The article emphasizes project status report templates for Agile and Waterfall projects specifically, along with industry-specific templates.
Q3. How do we measure the impact of project status reports?
The impact of project status reports can be measured based on their accuracy, comprehensibility, and timeliness. These factors are crucial in evaluating the effectiveness of the reports.
Q4. Why is feedback important in refining project status report templates?
Feedback is important for refining project status report templates because it helps identify potential areas of improvement. Continuous feedback helps in better serving stakeholders and facilitating successful project management over time.